Do you really need to work 100-hour weeks for success?
In 2021, America’s top 10% of income earners made at least $129,181 a year—more than double the average individual income across the country.
When looking at differences between income groups, there are many preconceived notions about the work involved. But what are the actual average working hours for different income groups?
This graphic by Ruben Berge Mathisen uses the latest U.S. Census data to show the average working hours of Americans at different income levels.
Comparing Average Work Weeks
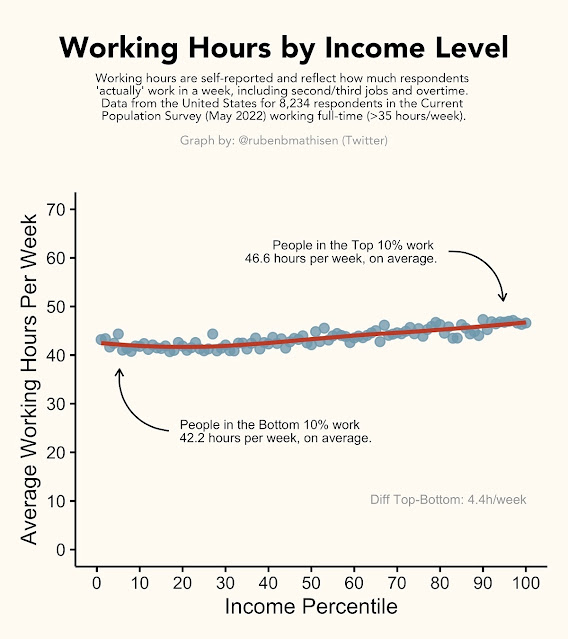
The data used for this graphic comes from the U.S. Census Bureau’s May 2022 Current Population Survey, which surveys more than 8,000 Americans from various socioeconomic backgrounds.
Importantly, the data reflects the average work hours that respondents in each income percentile “actually” work each week, and not what’s on their contract. This also includes overtime, other jobs, or side gigs.
According to the survey data, America’s top 10% income percentile works 4.4 hours more each week than those in the bottom 10%. And in surveys across other countries, though with hundreds of respondents instead of thousands, the discrepancy was similar:
While both income and wealth gaps are generally widening globally, it’s interesting to see that higher earners aren’t necessarily working more hours to achieve their increasingly larger salaries.
In fact, the top 10% in the 27 countries shown in the graphic are actually working around 1 hour less each week than the bottom 10%, at least among full-time workers.
Zooming Out: Average Working Hours per Country
Similarities arise when comparing average working hours across different countries. For starters, people living in poorer countries typically work longer hours.
According to Our World in Data, the average worker in Cambodia works about 9.4 hours a day, while in Switzerland, people work an average of 6 hours a day.
While many factors contribute to this discrepancy in working hours, one large factor cited is tech innovation, or things like physical machines, processes, and systems that make work more efficient and productive. This allows wealthier countries (and industries) to increase their output without putting in as many hours.
For example, from 1948 to 2011, farm production per hour in the U.S. became 16x more productive, thanks to innovations like improved machinery, better fertilizers, and more efficient land management systems.